Electrolytic Grinding of Carbides
Electrolytic grinding combines electrochemical machining and mechanical grinding to process carbides, with electrochemical machining playing the dominant role (80%-90%), while mechanical grinding accounts for only 10%-20%. The productivity of this method is 4-8 times higher than conventional mechanical grinding. Additionally, it allows for easy adjustment of electrical parameters, merging rough and fine machining into a single step, thereby shortening production cycles and reducing costs. This makes electrolytic grinding an ideal method for machining carbides.
Structure and Principle
Electrolytic grinding primarily consists of three main components: a DC power supply, a machine tool, and a hydraulic system, as shown in Figure 1.
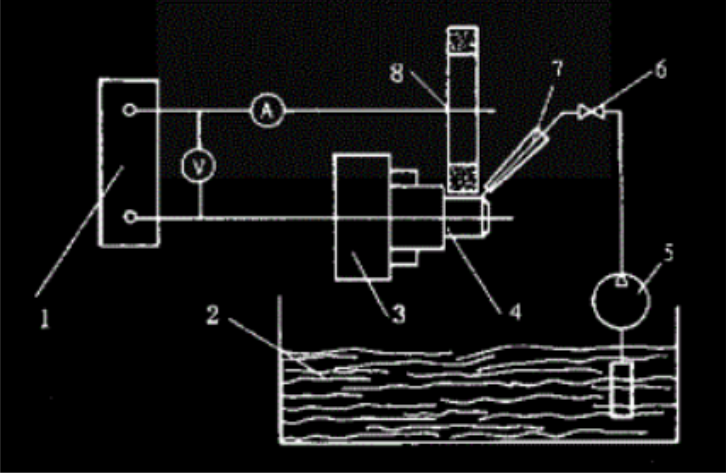
During electrolytic grinding, the carbide?workpiece is connected to the positive pole of the DC power supply, while the diamond conductive grinding wheel is connected to the negative pole. A certain contact pressure is maintained between the two, and an electrolytic gap is preserved between the workpiece and the protruding abrasive particles (diamond) on the grinding wheel. Electrolyte is supplied into this gap. When the power is turned on, an electrochemical reaction occurs on the workpiece surface, causing the carbide?to electrolyze and form a thin oxide layer (electrolytic film) on its surface. This oxide layer is much softer than the carbide?itself. The high-speed rotating diamond grinding wheel continuously removes this oxide layer, which is then carried away by the electrolyte. This exposes a fresh surface of the workpiece, allowing the electrolytic reaction to continue. The alternation between electrolysis and oxide layer removal results in the continuous machining of the carbide, forming a smooth surface with precise dimensions.
Electrochemical Reactions in Electrolytic Grinding of Carbides
carbides are primarily composed of hard carbides (WC, TiC) with a metal binder (Co), formed through pressing and sintering. According to electrochemical reactions, cobalt begins to dissolve at 1.2V, forming Co(OH)?:
?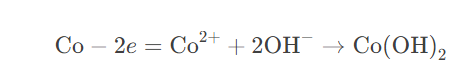
Tungsten carbide starts to dissolve at 1.7V, while titanium carbide begins to dissolve at 3.0V:
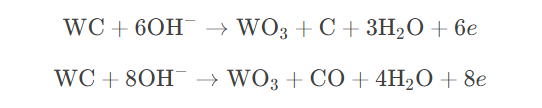
The electrolytic efficiency is the percentage of theoretical electrolysis to actual electrolysis. In electrolytic grinding, the electrolytic efficiency of carbides ranges from 70% to 90%.
Machining Parameters
Power Supply
The power supply for electrolytic grinding is a DC source with a voltage range of 4-14V and a current range of 50-3000A. The machining gap is approximately 0.03mm (roughly equal to the size of the abrasive particles).
Electrolyte
Electrolytic grinding is based on electrochemical dissolution. The choice of electrolyte significantly affects productivity, precision, and surface quality. After extensive testing, the following three electrolyte compositions were selected:
Electrolyte 2:
NaNO?: 6.3%, NaNO?: 0.3%, Na?HPO?: 2%, pH: 8-9, Na?B?O?: 1.4%, H?O: 90%
Electrolyte 3:
NaNO?: 5%, NaNO?: 1.6%, Na?HPO?: 1%, pH: 7-8, Na?B?O?: 1.5%, NaCl: 0.05%, C?H?(OH)?: 0.3%, H?O: Balance
The electrolyte is used at a temperature of 22-30°C and a pressure of 14-70kPa. The filter precision is 50-100μm, and the nozzle, installed close to the workpiece, is equipped with an air scraper.
Diamond Electrolytic Grinding Wheel
Diamond conductive grinding wheels are typically used for electrolytic grinding of карбидs due to their regular shape, high hardness, and ability to maintain a consistent electrolytic gap, resulting in high productivity. During fine grinding, mechanical grinding can be performed independently. Diamond electrolytic grinding wheels can be categorized into metal-bonded and electroplated diamond wheels. The former is used for flat and cylindrical grinding of carbide?molds, while the latter is used for electrolytic form grinding of large batches of single-shaped workpieces and internal cylindrical grinding of small holes. The grinding pressure is generally around 30N/cm2. The linear speed of the grinding wheel is typically 1200-2100 m/min, and the contact length with the workpiece should not exceed 19mm to prevent electrolyte boiling.
Material Removal Rate and Precision
The material removal rate of carbides is proportional to the current density. Under specific alloy materials, electrolyte combinations, and electrolyte boiling points, the current density is limited by the anode dissolution rate. The productivity of electrolytic grinding of carbides is generally 0.16cm3 per 100 A/min. At a current density of 77.5A/cm2, the feed rate for face grinding is 25mm/min, with a typical dimensional accuracy of ±0.025mm per pass. If an additional mechanical grinding pass is performed without electrolysis, the accuracy can reach ±0.002mm. When grinding external contours, the corner radius on the workpiece is about 0.025mm, while the roundness radius for internal contours is limited to 0.25-0.38mm. The material removal rate in electrolytic grinding is 4-8 times higher than that of conventional grinding methods.
Surface Quality
The surface roughness achieved by electrolytic grinding of carbides is generally Ra 0.2-0.8μm, but it can reach Ra 0.025-0.1μm. The surface of the workpiece resembles that obtained by metallographic polishing, and the hardness of the workpiece does not affect the surface quality. During machining, the processed surface does not develop internal stresses or heat-affected zones, resulting in high surface integrity.
Equipment and Tools
The grinding machine must have sufficient rigidity to maintain precision even under a bending stress of 1 MPa between the grinding wheel and the workpiece. The machine requires corrosion-resistant accessories for pressurizing and filtering the electrolyte. Control equipment, fixtures, and mechanical and electrical systems should be made of suitable materials or coated to operate in a salt spray environment. Conductive diamond grinding wheels are preferred for electrolytic grinding, although non-conductive abrasive wheels can also be used, albeit with less effectiveness. The electrolyte nozzle is typically made of heat-resistant organic glass or equivalent insulating materials. Workpiece fixtures are made of copper or copper alloys. The design should ensure that the cathode and anode parts are insulated during electrolytic grinding to maintain proper machine operation.
Discussion of Key Process Parameters
Current Density and Voltage
In electrolytic grinding, current density is the primary factor determining productivity. Productivity increases with higher current density, but excessively high or low current densities can reduce machining precision and surface quality. In practice, voltage should not be increased indefinitely, as excessively high voltages can cause spark discharge, affecting surface quality. For carbide?electrolytic grinding, the optimal current density is 110 A/cm2, with practical current densities ranging from 15-60 A/cm2 and voltages from 7-10V. For rough grinding, the current is 120-300 A/cm2, while for fine grinding, it is 5-6 A/cm2.
Machining Gap
At a given voltage, a smaller machining gap results in higher current density, increased productivity, and improved surface flatness and precision. However, if the gap is too small, the electrolyte may not distribute evenly, leading to spark discharge and increased wheel wear. The typical machining gap is 0.025-0.05mm.
Grinding Pressure
Increasing grinding pressure enhances productivity, but excessive pressure reduces the electrolytic gap, increasing the risk of spark discharge. Conversely, insufficient pressure leads to incomplete removal of the oxide layer, reducing both efficiency and surface quality. Therefore, grinding pressure should be set to avoid spark discharge while ensuring complete oxide layer removal. The recommended grinding pressure is 0.2-0.5 MPa.
Contact Area Between Workpiece and Grinding Wheel
A larger contact area allows the DC power supply to deliver higher current, increasing productivity while maintaining good surface quality. Therefore, during electrolytic grinding, the grinding wheel and workpiece should maintain the largest possible contact area.
Grinding Wheel Speed
Increasing the grinding wheel speed ensures adequate and rapid electrolyte supply in the gap, enhancing mechanical grinding and productivity. However, the speed should not be excessively high. The typical linear speed of the grinding wheel is 1200-2100 m/min.
Electrolyte Supply
The electrolyte flow rate should ensure sufficient and uniform entry into the machining gap. For vertical electrolytic surface grinders, the flow rate is typically 5-15 L/min, while for cylindrical grinders, it is 1-6 L/min. The installation of the electrolyte nozzle is crucial, as it helps confine the electrolytic action to the machining gap between the grinding wheel and the workpiece. The nozzle must be firmly installed close to the outer surface of the grinding wheel and equipped with an air scraper to break the air layer on the rotating wheel’s outer edge. The electrolyte pressure is generally 14-70kPa, and the temperature is controlled between 19-33°C.

Вывод
High Productivity
Electrolytic grinding of carbides offers 4-8 times higher productivity than conventional mechanical grinding, especially when the contact area between the conductive diamond grinding wheel and the carbide?workpiece is increased.
Excellent Surface Quality
Electrolytic grinding of carbides achieves high surface quality, with typical surface roughness of Ra 0.4μm or better, and can reach Ra 0.025μm, producing a mirror-like finish. Increasing the machining current does not significantly affect surface quality. Additionally, the processed surface does not develop internal stresses or heat-affected zones, resulting in high surface integrity unmatched by other machining methods.
High Precision
With advancements in carbide?electrolytic grinding, the use of diamond electrolytic grinding wheels that can perform both electrolytic and mechanical grinding allows for high precision. After electrolytic grinding, the power can be turned off, and mechanical grinding can be performed to achieve precision comparable to conventional mechanical grinding.
Low Grinding Wheel Wear
In electrolytic grinding, the abrasive particles in the grinding wheel primarily maintain the electrolytic gap and remove the oxide layer, reducing abrasive wear. The wear of diamond grinding wheels in electrolytic grinding is significantly lower than that in conventional mechanical grinding.
In summary, electrolytic grinding of карбидs offers unique advantages over conventional machining methods, significantly improving productivity, surface quality, and precision, making it an ideal method for machining carbides.









