Powder metallurgy is mainly applicable to the auto industry, equipment manufacturing industry, metal industry, aerospace, military industry, instrumentation, hardware tools, electronic appliances and other fields.
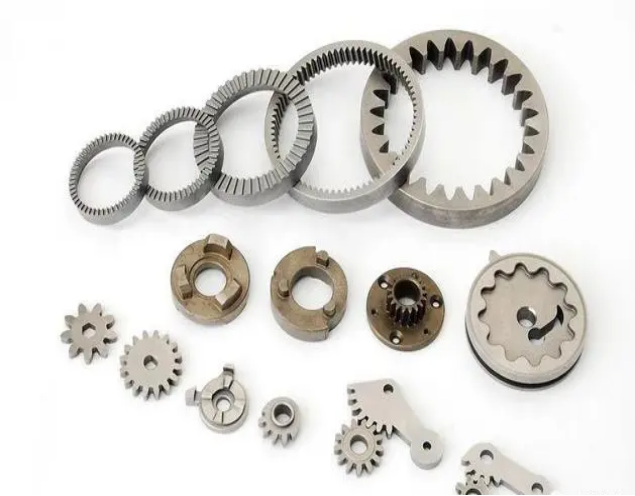

Metal powders commonly used in powder metallurgy include iron, copper, aluminum and their alloys. During the manufacturing process, the content of impurities and gases shall not exceed 1% ~ 2%, and the particle size of the powder shall not exceed 5 μ m~10 μ m. Otherwise, the quality of the products will be affected. The apparent geometry of the powder particles. The common ones are spherical, columnar, needle like, plate-like and sheet-like, which can be determined by observation under a microscope.
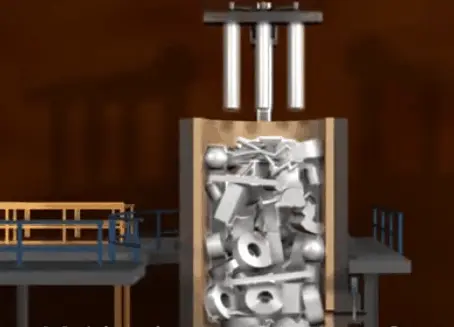
1. Arc melting in
The arc of direct heating arc melting is generated between the electrode rod and the melted charge, and the charge is directly heated and melted by the arc
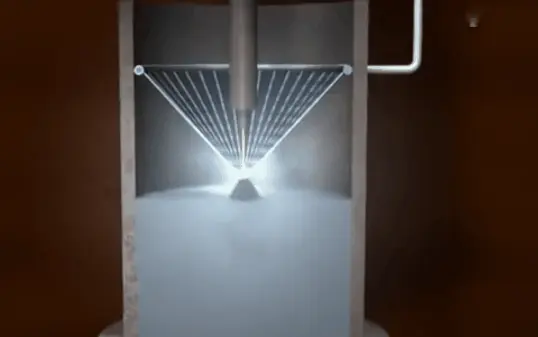
2. Ultra high pressure water atomization pulverization
The working principle of the ultra-high pressure water atomization pulverizing device is to melt metal or metal alloy under atmospheric conditions. Under the condition of gas protection, the metal liquid will be atomized and broken into a large number of fine metal droplets by the ultra-high pressure water flow through the nozzle in the process of flowing down through the insulating tundish and the guide pipe, In the process of flight, fine droplets form sub spherical or irregular particles under the combined action of surface tension and rapid cooling of water, so as to achieve the purpose of powder production.

3. Anneal
The pre annealing of the powder can reduce the oxide, reduce the content of carbon and other impurities, and improve the purity of the powder; At the same time, the work hardening of the powder can be eliminated and the crystal structure of the powder can be stabilized. The annealing temperature is usually 0.5 to 0.6k of the melting point of the metal, depending on the type of the metal powder. Generally, the annealing temperature of electrolytic copper powder is about 300 ℃, and that of electrolytic iron powder or electrolytic nickel powder is about 700 ℃, which cannot exceed 900 ℃. Annealing is generally conducted in a reducing atmosphere, and sometimes in a vacuum or inert atmosphere.
4. Grading
The process of dividing powder into several grades according to particle size. Grading makes it easy to control the particle size and particle size distribution of the powder during batching, so as to meet the requirements of the forming process. Standard screen is commonly used for grading.
5.Mixture
Refers to the process of homogenizing two or more powders with different components. The powder or mixture is mechanically mixed uniformly without chemical reaction. Plasticizers (gasoline, rubber solution, paraffin, etc.) used to improve the strength of compacts or prevent segregation of powder components. Hard zinc acid, molybdenum disulfide, etc., lubricants used to reduce the friction between particles and between the compact and the mold wall, and lubricants used to reduce the friction between particles and between the compact and the mold wall

6. Shaping
It is the process of transforming powder into product. The common forming methods are die pressing, rolling, extrusion, isostatic pressing, loose packing sintering, slurry casting, etc.

7. Sintering
1、 The sintering methods are different for different products and different properties. It is classified according to the composition of raw materials. Sintering can be divided into unit system sintering, multi-system solid-phase sintering and multi-phase sintering
a. Element system liquid phase sintering.
Unit system sintering is generally different from pure metals (such as refractory metals and pure iron soft magnetic materials)
b. Multicomponent solid-phase sintering is made of
Solid phase sintering is performed in a sintering system composed of two or more components in which the melting point temperature of the low melting component is lower than or equal to the melting point temperature. Such as Cu Ni, Fe Ni, Cu Au, W-Mo, Ag Au, Fe Cu, W-Ni, Fe-C, Cu-C, Cu-W, Ag-W, etc
2It is classified according to different feeding methods. It can be divided into continuous sintering and batch sintering

8. Post treatment before powder metallurgy
It refers to the further treatment after sintering of the compact, and determines whether post-treatment is required according to the specific requirements of the product. The commonly used post-treatment methods include re pressing, impregnation, heat treatment, surface treatment and cutting.
a Re pressing
Pressure applied treatment to improve the physical and mechanical properties of sintered body, including finishing and shaping. Finishing is the re pressing to achieve the required size. The sintering body is pressed by the finishing die to improve the accuracy. Shaping is the re pressing to achieve a specific surface shape. The product is pressed by the shaping die to correct the deformation and reduce the surface roughness value. Re pressing is applicable to products with high requirements and good plasticity, such as iron-based and copper based products.GIF

b Impregnation
The method of filling the pores of sintered body with non-metallic materials (such as oil, paraffin and resin). The common impregnation methods are oil impregnation, plastic impregnation, molten metal impregnation, etc. Oil immersion is to immerse lubricating oil in the sintering body to improve its self-lubricating performance and prevent rust. It is commonly used in iron and copper based oil-bearing. The impregnated plastic is made of polytetrafluoroethylene dispersion. After curing, it can realize oil-free lubrication. It is commonly used for metal plastic friction reducing parts. Immersion in molten metal can improve the strength and wear resistance. Copper or lead immersion is often used for iron-based materials.
c Heat treatment
The method of heating the sintered body to a certain temperature and then controlling the cooling method to improve the product performance. The commonly used heat treatment methods include quenching, chemical heat treatment, thermal mechanical treatment, etc. the process method is generally similar to that of dense materials. For iron-based parts that are not impacted but require wear resistance, integral quenching can be adopted. Since the existence of pores can reduce the internal stress, generally tempering is not required. And the iron-based parts requiring external hardness and internal toughness can be quenched or carburized. Hot forging is a common method to obtain compact parts. Hot forged products have fine grains and high strength and toughness.
d Surface treatment
The commonly used surface treatment methods include steam treatment, electroplating, zinc dipping, etc. The steam treatment is performed when the workpiece is in the range of 500 ~
The surface process of heating in hot steam at 560 ℃ and keeping it for a certain time to form a dense oxide film on its surface and pores. It is used for iron-based products requiring rust prevention, wear resistance or high-pressure penetration. Electroplating applies the electrochemical principle to deposit a solid coating on the surface of products, and the process method is the same as that of dense materials. Electroplating is used for products requiring rust prevention, wear resistance and decoration. In addition, the shape of the sintered body can be further changed or the accuracy can be improved by forging, welding, cutting, special processing and other methods to meet the final requirements of the parts. Special machining methods such as EDM, electron beam machining and laser machining, as well as surface engineering technologies such as ion nitriding, ion implantation, vapor deposition and thermal spraying, have been used for post-treatment of powder metallurgy products, further improving production









